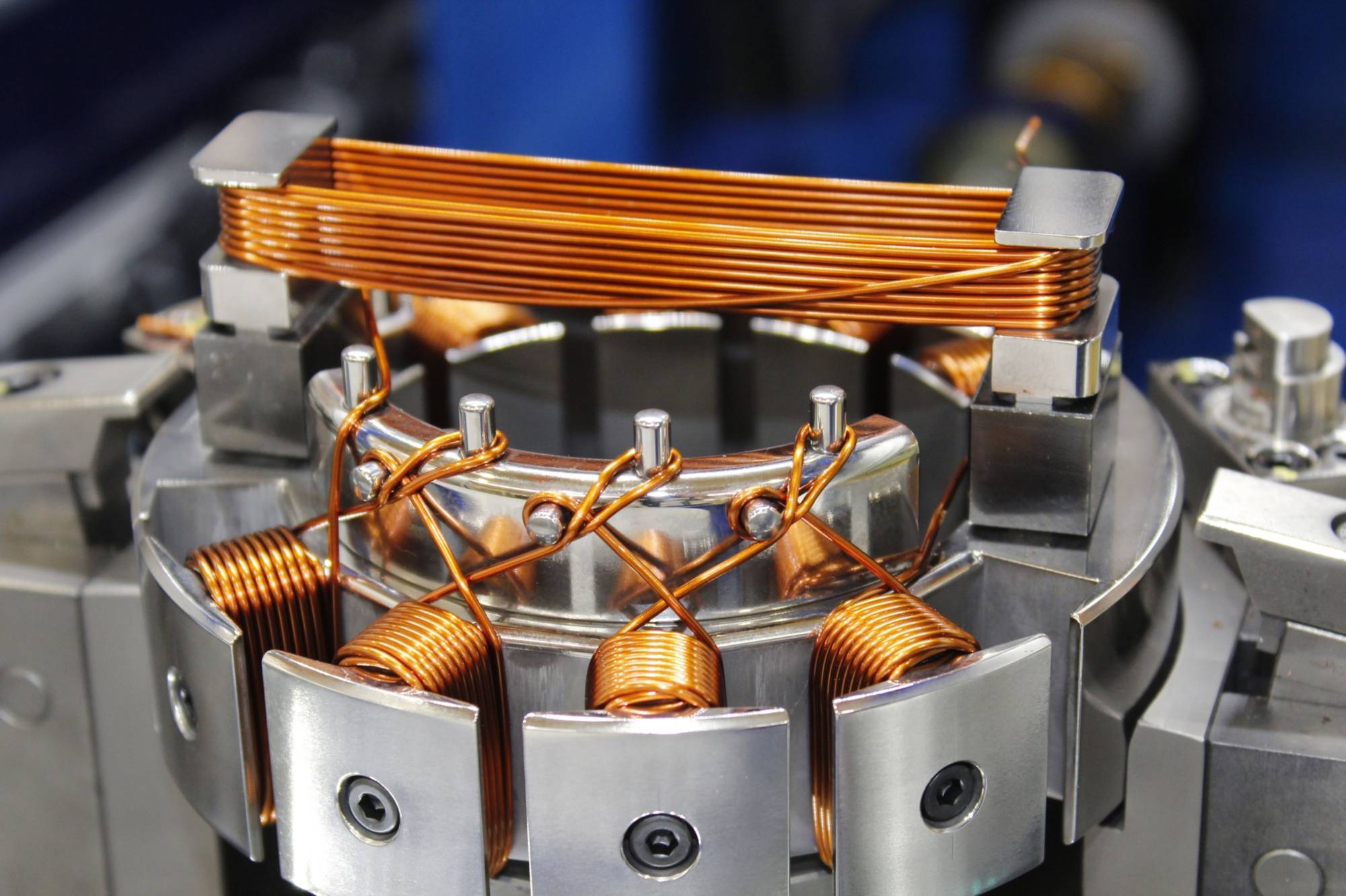
Winding technology is one of the most foundational yet overlooked areas of manufacturing. Whether you’re talking about transformers, yarn, wire, or film, winding plays a pivotal role in shaping how materials are processed, packaged, and put to use across countless industries. As manufacturing becomes increasingly automated and data-driven, winding systems have also undergone a significant transformation. What was once a mechanical process has now evolved into a precision-driven, software-controlled system at the heart of modern industrial production?
Contents
What Is Winding Technology?
Winding technology refers to the process of wrapping materials like wire, yarn, foil, or film around a core or spool in a systematic, controlled manner. It’s the backbone of countless industries, enabling everything from transformer construction to textile packaging. If you’ve ever seen a spool of thread or a roll of electrical wire, you’ve seen winding technology in action. The essence is simple: wind something in a controlled way. But beneath that simplicity lies a world of innovation.
Why Winding Is Crucial in Manufacturing
Imagine trying to produce an electric motor without tightly wound copper coils it wouldn’t work. The same goes for textile rolls or audio tapes. The precision and uniformity offered by modern winding machines directly affect the quality and performance of the end product. Before automation, artisans and workers manually wound threads, wires, and films using rudimentary tools. While effective, this method was labor-intensive and inconsistent. With the Industrial Revolution, winding machines became powered and standardized. In the digital age, machines are not just automated but also intelligent, offering predictive maintenance and self-correction features.
Types of Winding Technologies
Winding technologies have evolved significantly to meet the diverse needs of modern industries. Each type of winding technology is designed to handle specific materials, shapes, speeds, and end-use requirements. Whether it’s fine copper wire for electronics or heavy-duty textile yarn, precision and control are key in every variation.
Coil Winding: From speakers to inductors, coil winding is fundamental in electronics. Precision is everything sloppy winding results in inefficiencies and malfunctions. In the energy sector, large-scale coil winding for transformers is vital. The insulation, winding pattern, and tension directly affect energy loss and safety.
Textile Winding: Winding prepares yarns for weaving or knitting, ensuring consistent tension and package formation. From cones to cheeses and pirns, different yarn packages suit different textile machines and processes.
Film and Foil Winding: In food and pharmaceutical industries, film winding ensures smooth operation in packaging lines. Foil winding is used to construct capacitors—critical for electronics—where even a slight misalignment can cause failure.
Wire and Cable Winding: Wire winding machines ensure uniform spooling which is crucial for high-speed unwinding later during installation or manufacturing. Machines now detect defects, adjust speed, and even log production data in real time.
Advanced Winding Techniques
Winding technology has come a long way from the early days of manual coil winding to today’s highly automated, precision-driven systems. As industries demand more from materials — higher strength, greater uniformity, and ultra-fine tolerances the winding techniques themselves have evolved to meet these challenges. Let’s dive into some of the most advanced winding techniques that are revolutionizing how materials are processed and shaped.
Tension Control Systems
Too tight, and materials snap. Too loose, and they tangle. Modern winding relies on digital tension control systems to maintain the Goldilocks zone just right.
Precision Layering and Pattern Winding
Instead of random piling, pattern winding creates structured layers, improving aesthetics and performance, especially in yarns and coils.
Robotic and CNC-Based Winding Machines
Think of a robot with a laser focus. CNC winding machines follow exact coordinates to produce uniform coils, even on oddly shaped cores.
AI and IoT in Modern Winding Equipment
Winding machines are now “smart” equipped with sensors, AI algorithms, and IoT integration that allow real-time monitoring and remote troubleshooting.
Industry-Specific Applications
From electric vehicle motors to sensor coils, precision winding plays a key role in modern automotive innovation. Aircraft and defense systems rely on specialized windings in radar systems, actuators, and electrical systems. Capacitors, transformers, inductors none of these exist without precise coil winding. Miniature wound coils are used in imaging devices, implants, and diagnostics where error margins are practically zero.
The Evolution of Winding Machines
We’ve come a long way from crank handles. Today’s machines are intelligent, learning and adjusting without human input. Digital twins virtual replicas of winding systems help optimize setups, troubleshoot issues, and train operators without wasting material. Modern machines consume less power and waste fewer materials, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Challenges in Winding Technology
Some materials behave unpredictably under stress or tension. Machines must be versatile enough to handle variations. High speed often sacrifices quality. Winding technology plays a critical role in manufacturing across multiple industries — from textiles and electronics to plastics and medical devices. Despite its importance and the technological advances over the decades, winding still faces significant challenges that can affect efficiency, quality, and cost. Let’s explore some of the key hurdles the industry encounters today. Balancing both is a major challenge for manufacturers. While high-tech machines offer benefits, they also demand skilled technicians and regular upkeep.
Future Trends and Innovations
Winding technology has continually evolved to meet the growing demands of modern industries, and the future looks even more promising. With advances in automation, artificial intelligence, and sustainable manufacturing, winding systems are poised to become smarter, faster, and more adaptable. Let’s explore some of the key trends and innovations shaping the future of winding technology.
Smart Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is here, and winding is no exception. Machines talk to each other, share data, and optimize processes autonomously.
Customization and On-Demand Winding
Short-run, specialized products are on the rise. Machines now allow rapid changeovers and highly customized winding profiles.
Eco-Friendly Materials and Waste Reduction
Biodegradable films, recycled yarns, and efficient spooling techniques are shaping a greener future for winding.
Conclusion
Winding technology might not grab headlines, but it quietly powers the world literally and figuratively. From the coils in your smartphone to the fabric on your clothes, the evolution of winding is a tale of precision, adaptability, and innovation. As industries demand more speed, customization, and sustainability, winding technology is stepping up with smarter, greener, and more efficient solutions.
Recommended Articles:
Oster Tower Fan Servicing Centres in Hyderabad or Secunderabad Price – Full Guide 2025
Eaton CE16600H01 Rev No 1.3: Complete Guide for Industrial Control and Fire Pump Systems
Why is 91 94922 09490 T Rama Devi Important?
DQ08201 GP N: Everything You Need to Know in 2025